How to Know if You Have Diabetes 1

Living with undiagnosed diabetes is like trying to find your way in a maze without seeing. Your body sends out small clues that something is off. But figuring out these early signs can be tough.
How to Know if You Have Diabetes 1 Understanding your diabetes symptoms is key to taking charge of your health. This is especially true before serious problems start.
Blood sugar levels are very important for your health. If you notice changes in your weight or energy, it could be a sign. Kelly Clarkson’s journey shows how important it is to watch your health and lifestyle.
Diabetes symptoms can start slowly or suddenly. It’s important to pay attention to any changes in your body. Signs like feeling very thirsty or needing to pee a lot might seem small. But they could mean something big is going on with your health.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Early detection of diabetes symptoms is critical for effective management
- Blood sugar levels can fluctuate and impact overall health
- Recognizing warning signs helps prevent potential complications
- Lifestyle factors significantly influence diabetes risk
- Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring health
Understanding Diabetes: Types and Basic Information
Diabetes is a complex metabolic condition that affects millions of Americans. With over 38 million adults diagnosed, it’s key to know the different types of diabetes to manage your health well.
Diabetes changes how your body handles blood glucose, affecting insulin production and metabolism. Knowing the differences between diabetes types helps you spot health risks and get the right medical advice.
Type 1 Diabetes: An Autoimmune Challenge
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that often starts in children and young adults. In this condition, your pancreas makes little to no insulin. You’ll need to manage it with insulin therapy for life.
- Accounts for approximately 5-10% of diabetes cases
- Develops when immune system attacks insulin-producing cells
- Requires daily insulin injections
Type 2 Diabetes: The Most Common Form
Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90-95% of cases. It happens when your body doesn’t respond to insulin well or doesn’t make enough. It’s often linked to diet, weight, and genetics.
| Risk Factors | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|
| Obesity | Regular exercise |
| Family history | Balanced diet |
| Age over 45 | Weight management |
Gestational Diabetes: Pregnancy-Related Condition
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy, affecting about 8-10% of pregnant women. It’s a temporary condition that can affect both mom and baby, needing close monitoring.
“Early detection and management of gestational diabetes are key to preventing long-term health complications.” – American Diabetes Association
Though each diabetes type is different, they all share a common issue: blood glucose regulation problems. Understanding these differences helps you take steps to manage your metabolic health.
Common Early Warning Signs of Diabetes
Knowing the early signs of diabetes is key to managing it well. Your body gives hints that something’s off with blood sugar. Spotting these signs early can save your health.
Diabetes symptoms can sneak up on you. They often show up in ways you least expect. Here are some common signs:
- Extreme thirst that seems unquenchable
- Unexplained weight loss despite normal eating habits
- Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
- Frequent urination, especially during nighttime
- Slow-healing wounds or recurring infections
Fatigue is a big deal in diabetes. Your body can’t turn glucose into energy well. This leaves you feeling tired, even after you’ve been active. This constant tiredness can really affect your daily life and how productive you are.
“When your body can’t properly use glucose, every cell feels the energy deficit.” – Diabetes Research Institute
Weight loss that’s not planned can be a warning sign. If your body can’t use glucose right, it starts breaking down muscle and fat. This leads to losing weight without trying.
Look out for other signs like blurred vision, feeling hungrier than usual, and changes in your skin. Catching these symptoms early can help you manage your health better.
- Check your blood sugar levels regularly
- Maintain a balanced diet
- Engage in consistent physical activity
If you notice several symptoms, see a doctor. They can do tests and give you advice tailored to you.
How to Know If You Have Diabetes: Key Indicators and Testing
Finding out if you have diabetes early is key to keeping your health in check. Blood glucose tests give you important info about your body’s sugar levels and diabetes risk.
Diabetes screening uses different tests to check your blood sugar and health.
Blood Sugar Testing Methods
There are several ways to test blood glucose levels:
- A1C test: Shows your average blood sugar over 2-3 months
- Fasting blood sugar test: Checks your sugar after not eating for a night
- Random blood sugar test: Checks your sugar at any time
- Oral glucose tolerance test: Sees how your body handles sugar
When to Get Tested
How often you should get tested depends on your risk factors:
- Adults over 45 years old
- People with body image issues
- Those with a family history of diabetes
- Individuals with high blood pressure or cholesterol
Understanding Test Results
It’s important to understand your blood glucose test results:
| Test Type | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1C | Below 5.7% | 5.7–6.4% | 6.5% or above |
| Fasting Blood Sugar | 99 mg/dL or below | 100–125 mg/dL | 126 mg/dL or above |
“Early detection through blood glucose testing can significantly improve diabetes management and overall health outcomes.”
Knowing your test results helps you take care of your health. Talk to your doctor to understand your results and get advice on managing your health.
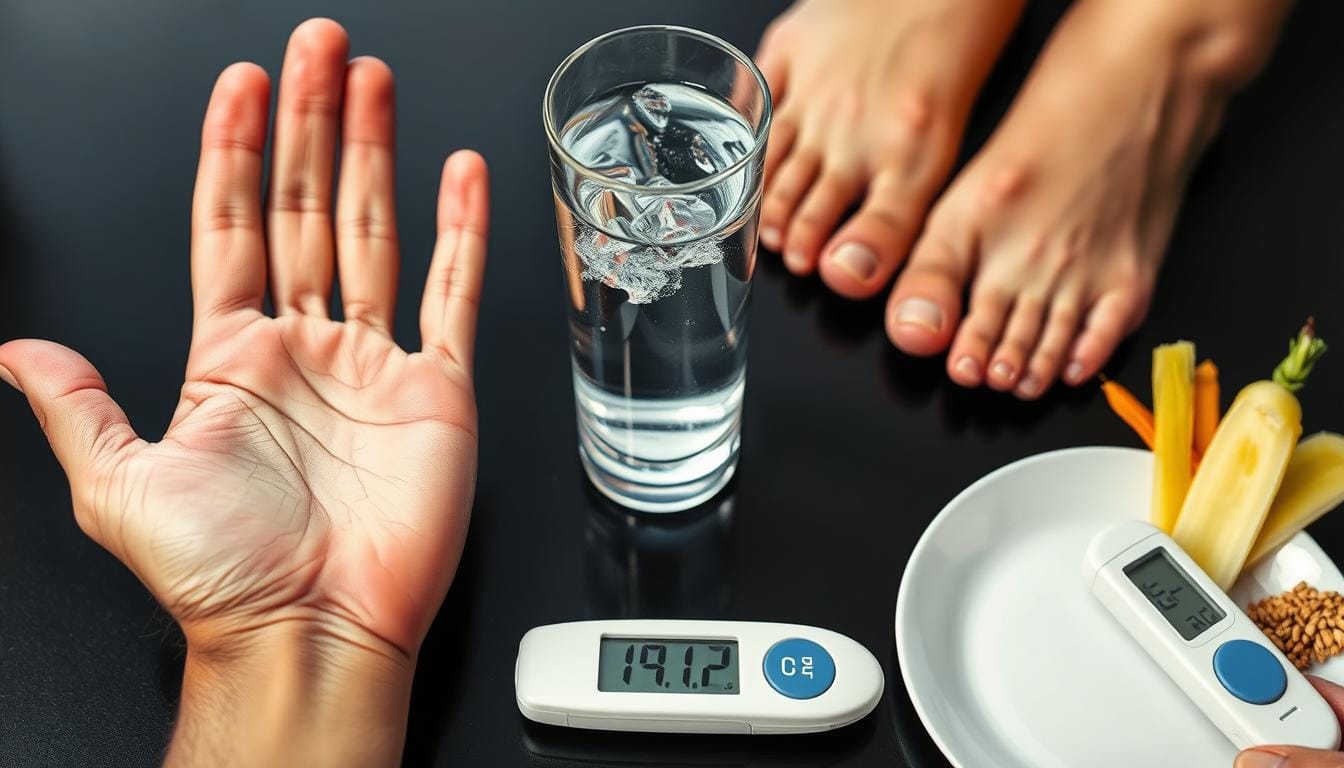
Frequent Urination and Increased Thirst: Primary Symptoms
When your body starts experiencing polyuria and polydipsia, it could be signaling a potential diabetes condition. Frequent urination and extreme thirst are critical warning signs that shouldn’t be ignored.
Typically, an average person urinates 4-7 times daily. With diabetes, this number dramatically increases. Polyuria occurs when your kidneys work overtime to eliminate excess blood sugar, leading to more bathroom trips and potential dehydration.
“Excessive thirst is your body’s way of compensating for fluid loss through frequent urination.”
Key symptoms of polyuria and polydipsia include:
- Urinating more than 8 times per day
- Waking up multiple times at night to use the bathroom
- Experiencing constant, intense thirst
- Drinking significantly more water than usual
Dehydration can quickly become a serious concern. A thyroid condition might also present similar symptoms, so professional medical evaluation is crucial. Your body’s signals of increased urination and thirst could indicate underlying metabolic changes requiring immediate attention.
Don’t dismiss these symptoms as mere inconvenience. They might be your body’s critical communication about potential diabetes or other metabolic disorders.
Changes in Appetite and Weight Fluctuations
Diabetes can change how your body uses energy, leading to unexpected weight changes and hunger shifts. It’s key to recognize these signs early to manage the condition.
Your body’s hunger and weight clues can hint at diabetes risks. These changes often signal that something is off inside your body.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexpected weight loss without dieting is a diabetes warning sign. Your body breaks down muscle and fat for energy when it can’t use glucose well, causing quick weight loss.
- Weight loss of 10-20 pounds unexpectedly
- Losing muscle mass quickly
- No changes in diet or exercise routines
Increased Hunger Patterns
Diabetes can make you feel hungry all the time, even after eating. This is because your cells can’t get glucose efficiently, sending out constant hunger signals.
“Hunger that feels insatiable might be more than just a big appetite—it could be a sign of underlying metabolic changes.” – Diabetes Research Institute
Changes in Eating Habits
Your eating habits can change a lot with diabetes. Some people might crave food more, while others might eat less.
| Eating Habit Changes | Potential Diabetes Indication |
|---|---|
| Constant thirst | High blood sugar levels |
| Frequent small meals | Unstable blood glucose |
| Sudden weight changes | Metabolic disruption |
While celebrity diets might seem appealing, listening to your body’s signals is more crucial. Regular health checks and paying attention to your body can help catch diabetes early.
Physical Changes and Body Symptoms
Diabetes can cause many physical changes that affect your health. Spotting these signs early helps manage your diabetes better and avoid serious problems.
Skin changes are often the first signs of diabetes. You might notice:
- Dry and itchy skin
- Slow-healing wounds
- Darkening of skin in specific areas (acanthosis nigricans)
- Increased risk of skin infections
Fatigue is another key sign of diabetes. If your body can’t handle glucose well, you’ll feel tired all the time. This tiredness can make it hard to stay motivated and productive.
“Understanding your body’s signals is the first step toward effective diabetes management.” – American Diabetes Association
Muscle loss is a big worry, especially for men with untreated diabetes. When insulin doesn’t work right, you lose muscle and get weaker.
Here are some tips to manage these changes:
- Regular medical check-ups
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Consistent exercise routine
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
Early detection and proactive management are key to minimizing the impact of diabetes on your physical health.
Vision Problems and Other Sensory Changes
Diabetes can harm your eye health and vision. It’s important to know about vision changes early. This helps prevent serious problems.
Diabetes can cause eye issues that affect your vision. Spotting these problems early is key. It helps protect your eyes and prevent damage.
Blurred Vision Symptoms
Blurred vision is a sign for people with diabetes. Blood sugar changes can swell your lens, causing vision problems. Look out for these symptoms:
- Sudden changes in visual clarity
- Difficulty focusing on objects
- Frequent prescription changes
- Experiencing vision fluctuations throughout the day
Eye Health and Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye issue for diabetics. It happens when high blood sugar damages your retina’s blood vessels. This can lead to vision loss.
“Approximately 26% of diabetic American adults experience diabetic eye disease, making it crucial to understand and monitor potential vision changes.”
To keep your eyes healthy, try these:
- Get regular eye exams
- Keep your blood sugar in check
- Live a healthy lifestyle
- Protect your eyes from UV rays
| Eye Condition | Symptoms | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetic Retinopathy | Blurred vision, dark areas, spots | Regular screenings, blood sugar control |
| Macular Edema | Wavy vision, color changes | Monitoring blood sugar, early intervention |
| Glaucoma | Tunnel vision, halo effect | Annual eye exams, medication management |
By making healthy lifestyle choices and taking care of your eyes, you can lower your risk of vision problems linked to diabetes.
Differences in Diabetes Symptoms Between Adults and Children
Pediatric diabetes and adult-onset diabetes have unique symptoms. Knowing these can help spot health risks early. This way, you can get the right medical help.
Children with type 1 diabetes show symptoms quickly and strongly. These symptoms can affect a child’s mental health and daily life.
- Pediatric diabetes symptoms:
- Extreme thirst
- Frequent urination
- Sudden weight loss
- Mood changes
- Potential bed-wetting
- Adult diabetes symptoms:
- Gradual onset of symptoms
- Slower progression
- More subtle physical changes
Age is key in how diabetes shows up and affects health.
“Early detection and understanding of age-specific symptoms are key to managing diabetes effectively.” – American Diabetes Association
Children with diabetes need close monitoring because their bodies are still growing. Regular doctor visits and blood tests are crucial for managing their diabetes.
Adults might get type 2 diabetes slowly, but children can see symptoms quickly. This shows why healthcare for kids and adults needs to be different.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
To prevent diabetes, we need to look at both genetics and lifestyle. Your risk of getting diabetes depends on many factors. You can change some of these through healthy choices.
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Many lifestyle choices affect your diabetes risk:
- Not being active can raise your risk by up to 50%
- Being overweight greatly increases your chance of type 2 diabetes
- Sitting too much lowers your insulin sensitivity
- Poor eating habits can disrupt your metabolism
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a big part in diabetes. Some groups are at higher risk:
- African Americans face a higher risk of type 2 diabetes
- Hispanic and Latino groups are also more vulnerable
- Having a family history of diabetes increases your risk
Preventive Measures
Stories of weight loss show that changing your lifestyle can lower diabetes risk. Important prevention steps include:
- Keeping a healthy weight
- Staying active
- Eating a balanced diet
- Getting regular health checks
“Prevention is always better than cure. Your daily choices can transform your health trajectory.”
Knowing your risk factors and making healthy lifestyle changes can lower your diabetes risk. This can also improve your overall health.
Conclusion
Understanding diabetes management is key to keeping you healthy and avoiding serious problems. Early detection is the most powerful tool in managing this condition. By recognizing symptoms and taking action early, you can greatly lower your risk of severe health issues.
Your health is very important. Regular doctor visits, blood sugar checks, and lifestyle changes are crucial in controlling diabetes. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases says type 2 diabetes can be managed well. This includes keeping a healthy weight and staying active.
Inspiring weight loss stories show that with effort and the right help, people can change their health for the better. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says lifestyle changes can greatly lower diabetes risks. Your path is unique, but with the right support and dedication, you can overcome diabetes challenges and live a healthy, fulfilling life.
Remember, diabetes is a journey, not a final destination. By staying informed, working with healthcare professionals, and staying positive, you can manage your condition well. This helps you avoid serious complications.
READ MORE : does nicotine cause cancer 01